Imaging sodium in the brain
-

Yasmin Blunck
Project Details
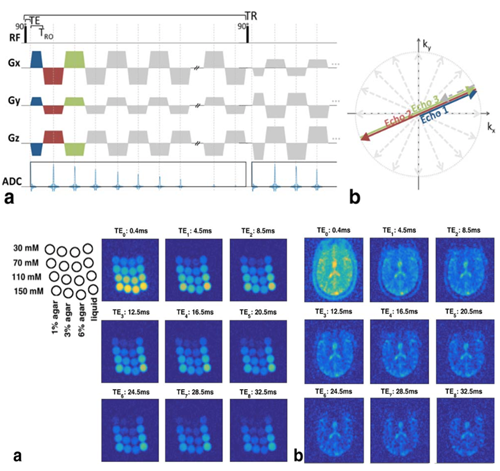
Sodium is critical for neuronal firing and is found in altered distributions in several brain diseases. While Sodium provides the second strongest MR-observable signal in biological tissue, its bulk signal strength is around ~20,000 times less than that of water making it difficult to reliably image, even at high field such as 7 Tesla. Our group has been developing new MRI sequences and post-processing techniques to image sodium and study sodium in different parts of the brain.
Research Group
Key Contact
For further information about this research, please contact the research group leader.
Department / Centre
Node
Royal Melbourne Hospital
MDHS Research library
Explore by researcher, school, project or topic.